5 timeless habits for better health

What are the symptoms of prostate cancer?

Is your breakfast cereal healthy?

When pain signals an emergency: Symptoms you should never ignore

Does exercise give you energy?

Acupuncture for pain relief: How it works and what to expect

How to avoid jet lag: Tips for staying alert when you travel

Biofeedback therapy: How it works and how it can help relieve pain

Best vitamins and minerals for energy

Should you take probiotics with antibiotics?
Medications Archive
Articles
What new opioid laws mean for pain relief
Dozens of states are cracking down on the amount of opioids doctors can prescribe.
Image: © Darwin Brandis/Getty Images
Overdoses of powerful painkillers called opioids kill more than 115 people per day in the United States. More than 42,000 people died from opioids in 2016, five times more than in 1999. The reason? Since several of these powerful painkillers became available in pill form several decades ago, doctors have been prescribing more than patients need. "It is estimated that a large part of leftover opioids are diverted to the street, either deliberately or through theft," says Dr. Edgar Ross, senior clinician at the Pain Management Center at Harvard-affiliated Brigham and Women's Hospital.
The misuse of opioids is a risk many states are no longer willing to take. The rules limit the amounts that medical professionals can prescribe for temporary (acute) pain from surgery, injury, or illness.
10 things you should know about common pain relievers
Which pain reliever should you take, acetaminophen or NSAIDs?
What you need to know about common pain relievers, from Tylenol to Aspirin. Once upon a time, easing pain was relatively simple: take two aspirin and call the doctor in the morning. Now there are many pain relievers to choose from (see "Pain relievers at a glance").
Willow bark was one of the earliest painkillers. Extracts or teas of willow bark have been used to treat fever and pain for more than 2,000 years. Unfortunately, the active ingredient, salicylic acid, is very hard on the stomach. In 1897, a German chemist working for the Bayer Company found a way to modify salicylic acid so it was less irritating to the stomach. The compound he created, acetylsalicyclic acid, was called Aspirin. It remained the premier over-the-counter painkiller until the development of acetaminophen in 1956 and ibuprofen in 1962. Since then, more than a dozen others have come onto the market.
What to do about the heartburn medication recall
Some drugs that contain ranitidine (best known as Zantac) have been found by the FDA to have unacceptable amounts of N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA), a possible cancer-causing chemical (which also triggered recalls of certain lots of the blood pressure drugs called angiotensin-receptor blockers).
On April 1, 2020, the FDA requested that all forms of ranitidine (Zantac, generic versions), including prescription and over-the-counter products, be removed from the market. They may contain unacceptable levels of a potential cancer-causing substance known as NDMA, or N-Nitrosodimethylamine. In some samples tested by the FDA, the impurity appears to increase over time, especially when stored at higher temperatures. So far, tests of other acid blockers do not show this potential increased cancer risk.
Older adults and medical marijuana: Reduced stigma and increased use
Cannabis use among older adults has been steadily increasing, due to lessening stigma and increased interest in using medical marijuana. But there are specific concerns for older people, so anyone considering this option should have a conversation with their doctor weighing the benefits and risks.
Have heart problems? Harvard researchers caution against marijuana use
News briefs
Smoking tobacco is a major cause of high blood pressure, heart disease, heart attack, and stroke. But did you know that smoking marijuana may also be associated with the same problems? A Harvard research review published Jan. 28, 2020, in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology found that more than two million U.S. adults with cardiovascular disease are smoking pot despite the risks, although they may not be aware of the potential link to heart problems. Studies on marijuana use have been limited, primarily because the substance has been illegal for decades. Scientists are calling for more research, since medical marijuana use is now legal in more than 30 states, and recreational use is legal in 11 states and the District of Columbia. "Until we have more answers about the connection between using marijuana and heart problems, you should consider avoiding smoking any form of pot if you have known heart disease or a high risk for a heart attack or stroke," suggests Dr. Deepak L. Bhatt, a study author and editor in chief of the Harvard Heart Letter.
Image: © Alexandrum79/Getty Images
Doctors’ pain pill prescribing habits at odds with current guidelines
Research we're watching
Doctors have been overprescribing opioids for chronic musculoskeletal pain, according to a December 2019 study in The Journal of Pain. Researchers looking at data from a survey conducted between 2007 and 2015 found that doctors more often prescribed pills, either non-opioid or opioid, rather than physical therapy, counseling, or other nondrug interventions — a practice that is directly at odds with what experts now recommend, including those in the CDC Guideline for Prescribing Opioids for Chronic Pain. At their first visit with the doctor, people were most often prescribed non-opioid painkillers (40.2%) or opioids (21.5%), followed by counseling, nonpharmacological treatments, and physical therapy. Study authors say this shows there is room for improvement through education. However, it's worth noting that the time period studied (2007 through 2015) preceded much of the recent work and advocacy aimed at reducing prescriptions of opioids.
Image: © robeo/Getty Images
Experimental drug lowers lipoprotein(a), a suspect in heart attacks
Research we're watching
A new kind of drug given by injection can lower blood levels of lipoprotein(a), or Lp(a), a fatty particle linked to a heightened risk of heart attack and narrowing of the aortic valve, according to a study published January 1 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Up to one in five people has a very high level of Lp(a), which is nearly completely determined by a person's genes. Lp(a) particles are similar to the better-known LDL cholesterol particles but with an extra protein coiled around each particle.
Can a slow heartbeat be dangerous?
Ask the doctor
Q. I'm in my 70s, and I get breathless when I climb stairs. Maybe that's normal at my age, but my doctor says the cause may be my slow heartbeat. Can a slow heartbeat be dangerous?
A. Yes, it could be. To explain why, let's begin with the basics. Your heart beats in order to pump blood around the body. The circulating blood brings the nutrition that every cell in your body needs, and it removes cellular waste material: blood brings the food and takes away the garbage. The effectiveness of the circulation depends on how much blood your heart pumps with each heartbeat and how many times per minute it beats. Even if each heartbeat pumps a lot of blood, if your heart doesn't pump often enough, your body won't get the blood it needs. And when you exert yourself, the body needs more blood.
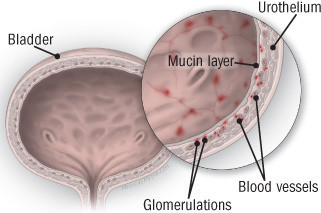
Diagnosing and treating interstitial cystitis
Also called painful bladder syndrome, this frustrating disorder disproportionately affects women.
Interstitial cystitis is a chronic bladder condition that causes recurring bouts of pain and pressure in the bladder and pelvic area, often accompanied by an urgent and frequent need to urinate — sometimes as often as 40, 50, or 60 times a day, around the clock. Discomfort associated with interstitial cystitis can be so excruciating that, according to surveys, only about half of people with the disorder work full-time. Because symptoms are so variable, experts today describe interstitial cystitis as a member of a group of disorders collectively referred to as interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. (In this article, we'll call it interstitial cystitis, or IC.)
Among the one to two million Americans with IC, women outnumber men by as much as eight to one, and most are diagnosed in their early 40s. Several other disorders are associated with IC, including allergies, migraine, irritable bowel syndrome, fibromyalgia (a condition causing muscle pain), chronic fatigue syndrome, and vulvodynia (pain or burning in the vulvar area that isn't caused by infection or skin disease).
What’s the best time of day to take your medication?
Timing may improve potency and help you cope with side effects.
We all want our medicines to be as effective as possible, and that requires effort on our part. It may be necessary to avoid taking pills with certain foods or drinks, and to check that medications won't interfere with each other.
And in some cases, it may be important to take a drug at a particular time of day. This approach, known as chronotherapy, is gaining attention as research suggests a relationship between when we take medications and how well they work.

5 timeless habits for better health

What are the symptoms of prostate cancer?

Is your breakfast cereal healthy?

When pain signals an emergency: Symptoms you should never ignore

Does exercise give you energy?

Acupuncture for pain relief: How it works and what to expect

How to avoid jet lag: Tips for staying alert when you travel

Biofeedback therapy: How it works and how it can help relieve pain

Best vitamins and minerals for energy

Should you take probiotics with antibiotics?
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up