5 timeless habits for better health

What are the symptoms of prostate cancer?

Is your breakfast cereal healthy?

When pain signals an emergency: Symptoms you should never ignore

Does exercise give you energy?

Acupuncture for pain relief: How it works and what to expect

How to avoid jet lag: Tips for staying alert when you travel

Biofeedback therapy: How it works and how it can help relieve pain

Best vitamins and minerals for energy

Should you take probiotics with antibiotics?
Staying Healthy Archive
Articles
Your New Year’s resolution: A gym membership?
What to consider when choosing a workout venue.
Image: vencavolrab/Thinkstock
If getting in shape tops your list of New Year's resolutions, you're in good company. During the first few months of the year, sign-ups at fitness centers and health clubs tend to trend upward. While these memberships can be costly, you may be able to find more affordable options or take advantage of discounts. But no matter what you pay, shelling out a monthly fee may encourage you to use the gym regularly to get your money's worth. If you do, your heart will likely reap the rewards: regular exercise is one of the best ways to boost cardiovascular health.
"The main advantage to joining a gym is to have access to a wide variety of exercise equipment," says Alex Petruska, a senior physical therapist at the Sports Medicine Center of Harvard-affiliated Massachusetts General Hospital. That includes machines for a cardiovascular workout, such as treadmills, elliptical trainers, stationary bikes, and stair steppers, as well as a variety of weight machines.
Online hospital ratings: Are they helpful?
A better understanding of these rating systems can help you know how and when to use them.
Image: NiroDesign /Thinkstock
Many people make it a habit to check online reviews before purchasing products and services. But not everyone realizes that you can also find online ratings of many hospitals throughout the United States.
Granted, choosing your hospital isn't always an option (in the event of a heart attack, for example). Location and insurance issues may also come into play. But if heart disease is a concern, do you know how your local hospital's cardiac care stacks up? What if you need a non-emergency procedure? Where's the best place to go?
Bringing awareness to aneurysms in the chest
Most often, bulges in the aorta near the heart are found by accident. Should you be screened for this rare yet dangerous condition?
Image: Nerthuz /Thinkstock
The aorta, the body's largest blood vessel, arises from the heart's left pumping chamber, then curves up and over the heart in a gentle arc. In some people, a weak spot in the aorta's wall causes the vessel to bulge outward like a worn-out bicycle tire. Called a thoracic aneurysm, this stealthy condition develops slowly and silently, rarely causing symptoms. And while some thoracic aneurysms are relatively harmless, others cause catastrophic problems. An estimated one in 10,000 people has a thoracic aneurysm, although the exact prevalence is unknown.
"Most thoracic aneurysms are discovered on an imaging test done for some other reason," explains Dr. Eric Isselbacher, associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and co-director of the Thoracic Aortic Center at Massachusetts General Hospital. For example, an aneurysm might be visible on an echocardiogram (heart ultrasound) done during testing for an irregular heartbeat. Because the condition is so uncommon, testing everyone for a thoracic aneurysm doesn't make sense. But certain people face a higher risk than others (see "Who needs to be checked?").
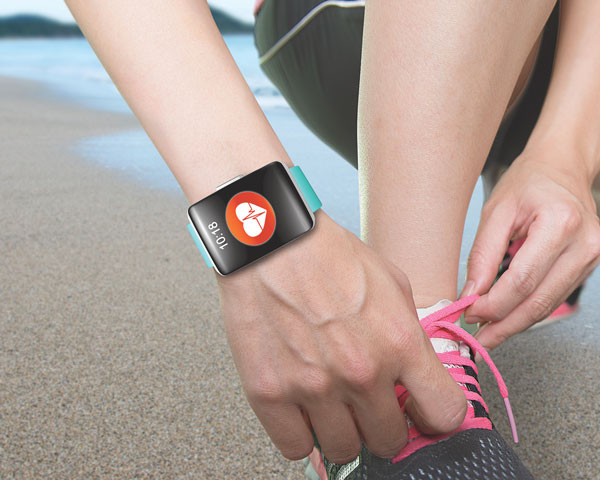
Are wristwatch-style heart rate monitors accurate?
Wristwatch-style fitness monitors use a sensor that detects blood flow through the skin to estimate a person’s heart rate. Some brands are more accurate that others, but none are as accurate as chest-strap monitors.
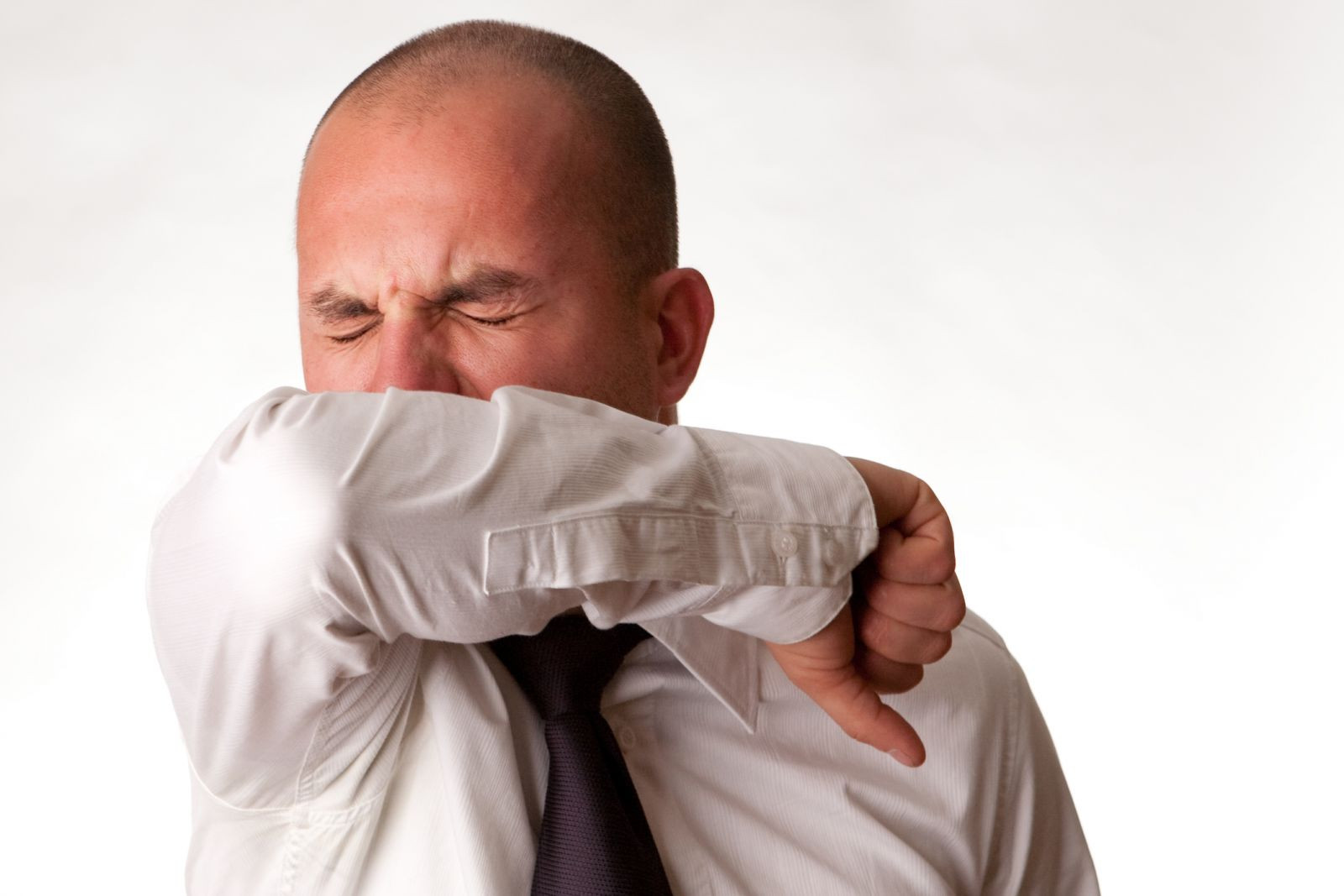
What causes a cough after a cold?
A persistent cough that remains after an infection has been treated can last for a month or two. There are several treatments that may offer relief, such as antihistamines or a bronchodilator inhaler.
When is it okay to split medication in half?
Splitting a pill into two equal halves is sometimes necessary when needing to adjust dosage, or as a means to save money buy purchasing higher-dose pills. However, splitting is not safe for all pills, so a person should always consult a pharmacist or doctor.
Looking for a few good men
There are many opportunities to join a clinical trial, and you may be surprised at what you can learn about your health.
Image: ggustavofrazao/Thinkstock
You no doubt have seen advertisements asking people to join a clinical trial and thought they don't apply to you. But perhaps you should reconsider.
"People have a vested interest in the outcome of research trials, since these studies address many issues they want to avoid or better manage, such as cancer, diabetes, blood pressure, and dementia," says Dr. Howard Sesso, an epidemiologist with the division of preventive medicine at Harvard-affiliated Brigham and Women's Hospital.
Stopping exercise for 10 days can decrease brain blood flow
Stopping exercise for 10 days can reduce brain blood flow by 20% to 30% in eight brain regions, including the hippocampus, which is responsible for learning and memory and is one of the first brain regions to shrink in Alzheimer’s disease.
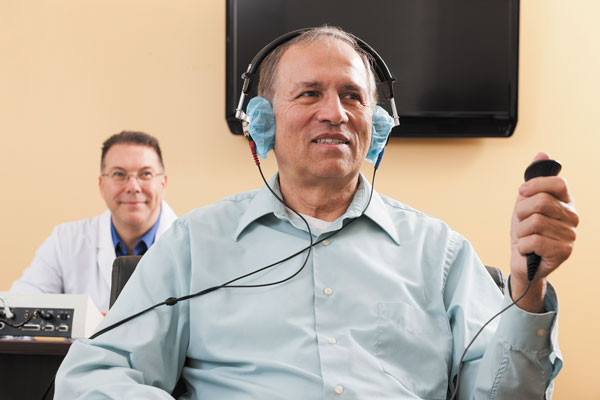
Now hear this: You may need hearing aids
These tiny devices can improve your communication, your relationships, and even your brain function, but only if you use them.
Image: Huntstock/Thinkstock
Age-related hearing loss affects about a quarter of people ages 65 to 74 and half of those ages 75 and older, according to the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders. Over all, though, it tends to be more male-oriented.
“By middle age, many men also have hearing nerve damage from long exposure to noises like power tools, music, and guns,” says Dr. Steven Rauch, an otologist with Harvard-affiliated Massachusetts Eye and Ear. Some career choices—like construction, manufacturing, or military service—also contribute.
What clinical trials can do for you
Participating in a medical study may benefit your health and perhaps that of millions of others.
Image: grandaded/Thinkstock
If you've ever considered donating your body to science—or granting science a temporary loan—now's the time to do it. Researchers are always recruiting patients for studies of new treatments and preventive strategies for diseases ranging from Alzheimer's to zoster (shingles). In the simplest terms, these studies compare existing approaches to newer ones in similar groups of people and determine which is more effective.
"Clinical trials are the vehicle by which we transfer things that we think into things that we know or don't know," says Dr. Jeffrey Drazen, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and editor in chief of The New England Journal of Medicine.

5 timeless habits for better health

What are the symptoms of prostate cancer?

Is your breakfast cereal healthy?

When pain signals an emergency: Symptoms you should never ignore

Does exercise give you energy?

Acupuncture for pain relief: How it works and what to expect

How to avoid jet lag: Tips for staying alert when you travel

Biofeedback therapy: How it works and how it can help relieve pain

Best vitamins and minerals for energy

Should you take probiotics with antibiotics?
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up