5 timeless habits for better health

What are the symptoms of prostate cancer?

Is your breakfast cereal healthy?

When pain signals an emergency: Symptoms you should never ignore

Does exercise give you energy?

Acupuncture for pain relief: How it works and what to expect

How to avoid jet lag: Tips for staying alert when you travel

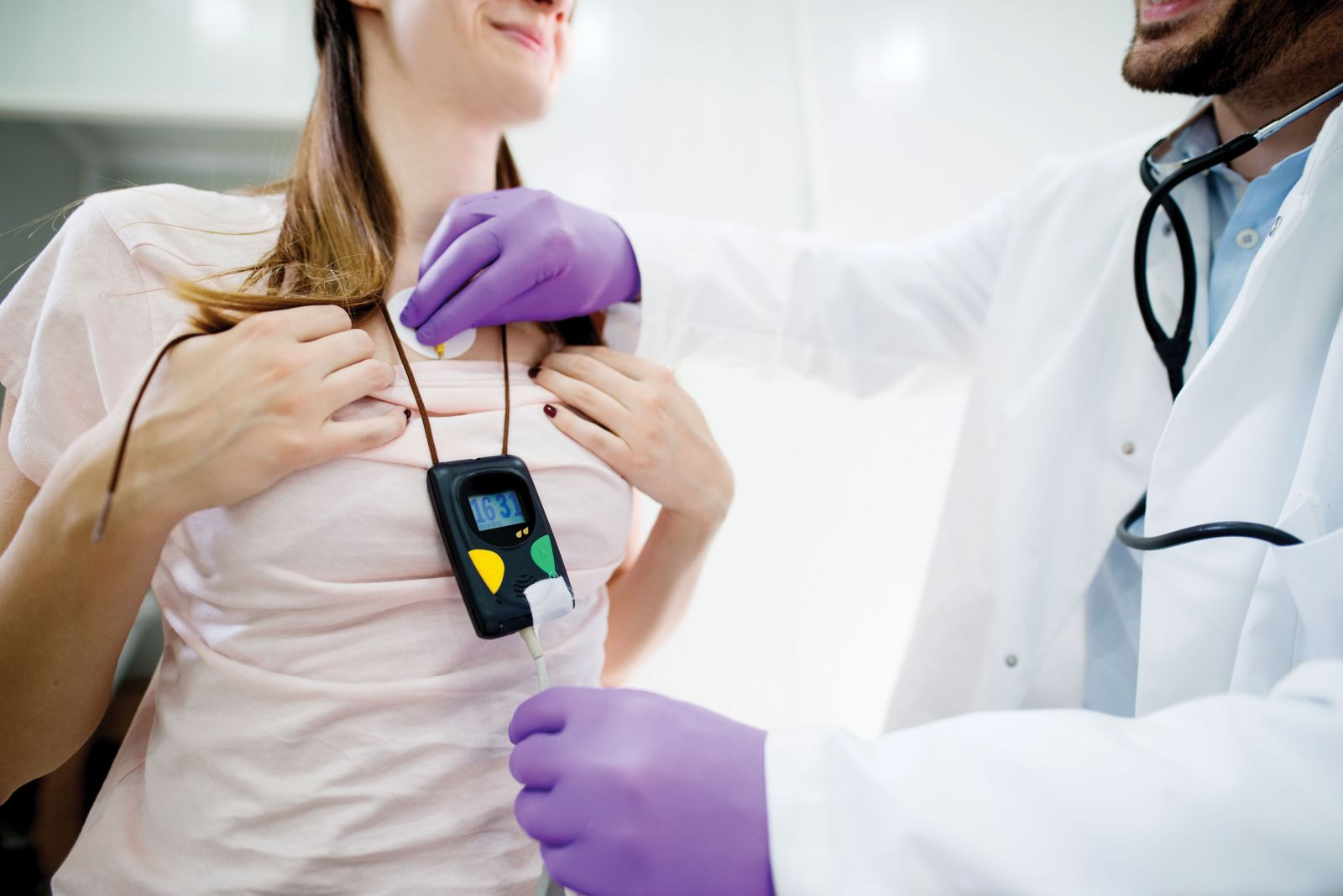
Biofeedback therapy: How it works and how it can help relieve pain

Best vitamins and minerals for energy

Should you take probiotics with antibiotics?
Sleep Archive
Articles
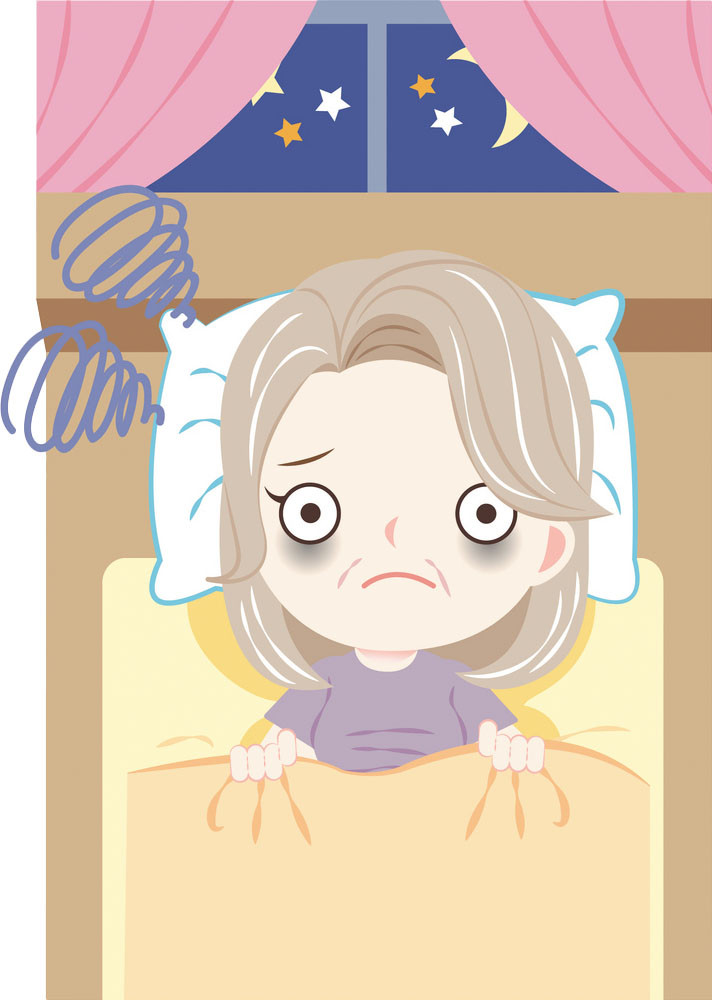
Study: Light pollution may trigger insomnia
Research we're watching
High exposure to bright, artificial outdoor lights during the night may result in sleepless nights for older adults. The more of this so-called light pollution that people were exposed to at night, the more they seemed to turn to medication to help them sleep, according to a study published in the Nov. 15, 2018, Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine. People in brightly lit areas, as judged by satellite data, also seemed to take those drugs for longer and took higher doses than people who weren't exposed to nighttime light.
To come to their conclusions, the researchers looked at data on more than 50,000 adults ages 60 or older from the National Health Insurance Service–National Sample Cohort, a database of information collected on people who participated in health screenings between 2002 and 2013 in South Korea. Researchers compared the people's nighttime light exposure and their use of two sleep drugs, zolpidem (Ambien) and triazolam (Halcion).
4 simple ways to boost your energy
Do you sometimes feel like the Energizer Bunny when his battery runs low? You might start the day strong, but by midafternoon, you can't quite keep going and going.
Fatigue afflicts everyone at one time or another. Assuming your doctor has ruled out serious medical causes, there are a few basic steps you can take to "recharge your batteries."
Shorter sleep may cause dehydration
Image: © miya227/Getty Images
In the journals
Adults who sleep only six hours per night may have a higher chance of being dehydrated, compared with those who sleep longer, according to recent research published online Nov. 5, 2018, by the journal Sleep. The findings suggest that some of the symptoms of inadequate sleep, such as fatigue, fuzzy thinking, and headache in the morning, may be due to dehydration.
Researchers looked at the risk of dehydration in approximately 20,000 U.S. and Chinese adults. In both populations, people who reported sleeping six or fewer hours had up to a 59% higher risk of dehydration compared with those who slept seven to eight hours on a regular basis. The researchers speculated that the finding may reflect the nightly rhythm of a hormone called vasopressin. During sleep, the pituitary gland in the brain uses vasopressin to signal the kidneys to retain fluid in the body rather than excreting it through urine.
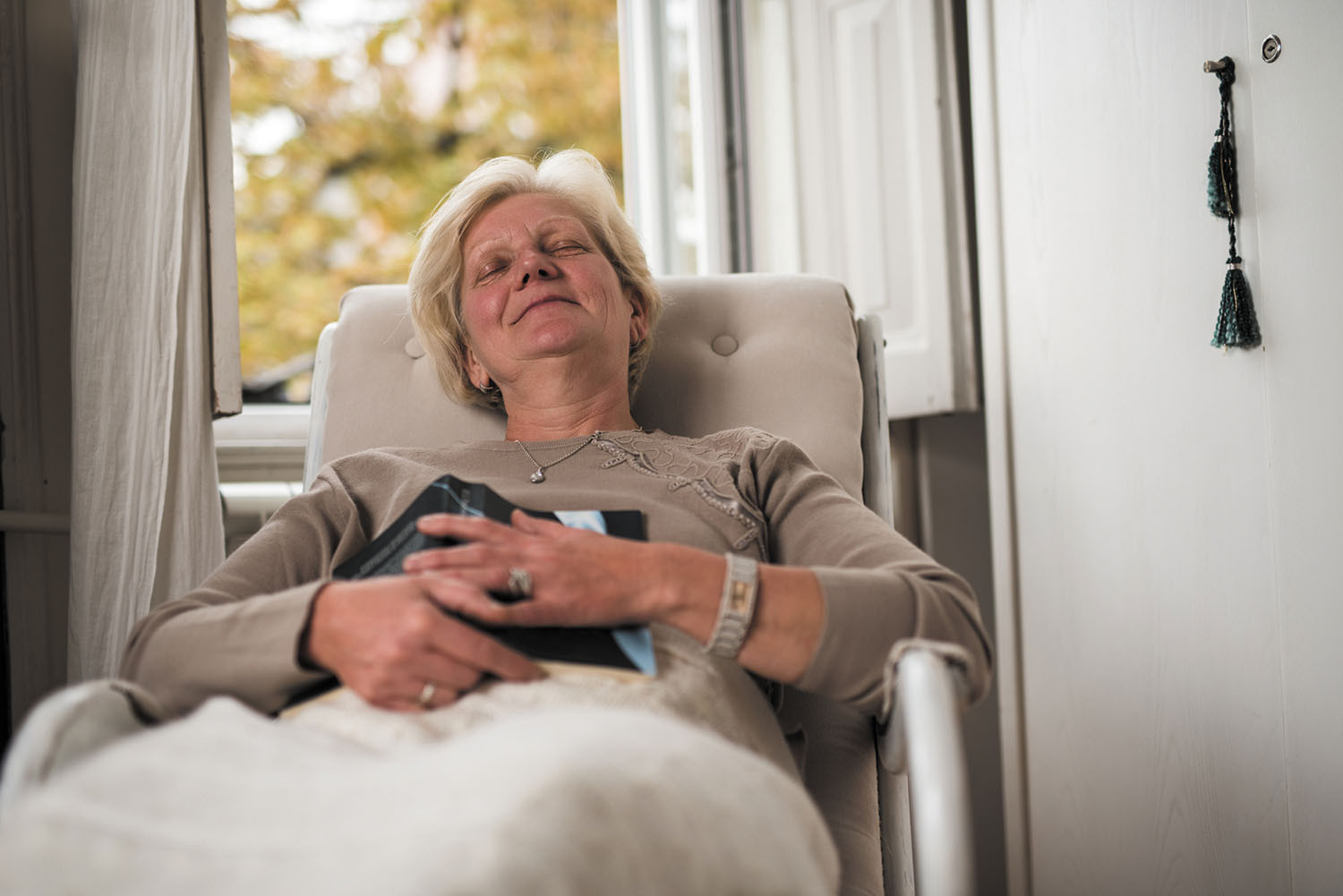
Is it dangerous to sleep sitting up?
Ask the doctors
Image: © BraunS/Getty Images
Q. After I had cataract surgery and facial surgery, I loved sleeping in my recliner for days on end. Does sleeping while sitting up put my brain and vital organs at risk since the blood supply has to travel uphill?
A. Sleeping sitting up in a recliner shouldn't be harmful. It could, in some cases, raise your risk of deep-vein thrombosis, a blood clot in a limb that can occur if your arms or legs are bent and you are motionless for hours. This sometimes occurs in people who sit still for long periods of time in an airplane seat. But provided you are comfortable and can recline back slightly, there should be few risks to sleeping upright, assuming it doesn't interfere with your ability to get a good night's sleep.
Heart palpitations: Mostly harmless
Occasionally these heart rhythm disruptions signal a more serious condition.
Image: © dusanpetkovic/Getty Images
Lately you've felt like a flipping fish is stuck inside your chest. You feel fine otherwise, but there it is again — flip, flop. It's gone as fast as it appears. But you're starting to worry: is it a sign of a serious heart problem?
Chances are what you're feeling is a condition called heart palpitations, which are usually harmless blips in the heart rhythm, explains Dr. Peter Zimetbaum, a professor of cardiovascular medicine at Harvard Medical School. Only occasionally are these rhythm disturbances the sign of a more serious heart problem that should be checked out.
Daytime sleepiness may indicate a higher risk for Alzheimer’s disease
In the journals
Are you excessively sleepy during the day? If so, you may have a higher risk of Alzheimer's disease, according to a recent study published online Sept. 5, 2018, by the journal Sleep.
Scientists asked 124 healthy older adults, average age 60, about how often they felt drowsy or fell asleep during the day when they would rather be awake, as well as their napping habits. The group then had regular PET scans over the next 15 years to look for beta-amyloid in the brain, high amounts of which are a hallmark for Alzheimer's.
Drugstore sleep aids may bring more risks than benefits
Explore more effective alternatives to help you get a good night's rest.
Image: © miya227/Getty Images
You've spent the past few nights staring at the ceiling, thinking about your grocery list, lining up your tasks for the next day, or obsessing about your problem du jour — but what you really want to be doing is sleeping soundly. You're in the pharmacy and notice an array of over-the-counter sleep aids, and you're tempted. Will taking one help you get that deep slumber you crave?
Before you reach for that bottle, you might want to reconsider.
5-minute fixes for better health
Taking on a new health regimen can be daunting. Accomplishing smaller tasks that contribute to health may be easier to achieve.
You know what you're supposed to do: exercise daily, ditch junk food, get more sleep, and stay vigilant about every aspect of your health. It's a nonstop commitment that seems like a major undertaking if you've fallen behind. But putting off a healthy lifestyle increases the risk for developing chronic disease and jeopardizes your independence.
Rather than identifying big ways to improve your health, and then procrastinating, focus on small tasks that won't overwhelm you. Try a quick fix once in a while — or all the time if it applies. The more you do, the better you'll feel.
Better sleep, naturally
The world looks very different at 3 a.m. when you're lying in bed staring at the ceiling or the clock. "How will I make it through tomorrow without any sleep?" you worry. You may wonder how to sleep better every night. If you regularly can't get to sleep - or stay asleep - and it's affecting you during the day, then you may have insomnia.
Prescription or over-the-counter sleep aids can help you drift off, but these drugs also have side effects. These include morning drowsiness, which can make activities like driving or using machinery dangerous, and an increased risk for falling. There are other ways to sleep better than medications.

5 timeless habits for better health

What are the symptoms of prostate cancer?

Is your breakfast cereal healthy?

When pain signals an emergency: Symptoms you should never ignore

Does exercise give you energy?

Acupuncture for pain relief: How it works and what to expect

How to avoid jet lag: Tips for staying alert when you travel

Biofeedback therapy: How it works and how it can help relieve pain

Best vitamins and minerals for energy

Should you take probiotics with antibiotics?
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up